
OPEN
The OPEN command is used to enter an existing database. The OPEN refers to an
Interface name which is then used to "plug you into" the database.
Syntax:
OPEN/options
Application-Interface-name
Notation standards Options Answers
Options:
A -Open
even though there are cycle errors - only to unload records
P -Open
the procedure catalog, not the database
R -Open
in read-only mode
S -Open
for exclusive use
X -Suppress
the command response
Y -Do
not alter the command answers cells
Answers:
Ctl.Ans1 =Zero
Ctl.Ans2 =Zero
Ctl.Ans3 =Zero
Notes:
An Application Interface is the only avenue by which you plug into any given
database. When you compile a Database Definition a default Application
Interface file is created. Alternatively, you can create one or more of your
own Application Interfaces. In either event, it is the Application Interface that is the object
of the OPEN command, and it can be referred to with a full path file name.
The Procedure Catalog is associated with the Application Interface, so once a
database is open, the user has access to all of the Procedures, Menus, Screens
and Reports of that application.
All collections are cleared upon OPEN.
OPEN looks for the existence of a CONFIG file and
does what it says during the process of opening. If they are not part of a
CONFIG file, the following MODEs get reset to default values by OPEN. So if you
want something other than the default for any of these, you should have them in
a CONFIG file or insure that they get re-invoked after the OPEN. To re-invoke
after the OPEN, a good place to put them is in the APPLICATION procedure. They
are:
MODE STOP
MODE ESC
MODE RESTART
OPENing from the File Menu
When you compile DBD's and AI's, information about the location of these
elements goes into a dictionary, the contents of which is used to produce a
listpick of existing databases that is used when you OPEN a database from the
File Menu. For example:
If you pull down the File Menu and select the first choice, "Open Data
Base..." you will see something like this:
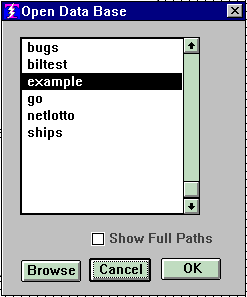
This is a list of all your current databases. (When you see this for the first
time after installing Thunderbolt, there will be only one choice in it, and
that choice will be EXAMPLE .)
The idea is that the user selects the database they wish to open and clicks OK.
If the database you wish to open is not in this list, you can use the BROWSE to
go find it and select it. After that it will be in the list.
When a database is OPENed in this manner (that is, opening from the File Menu
rather than going directly to DCL with no database open and keying in the OPEN
yourself) there is one other thing that happens. And that is that it
automatically looks for a procedure named APPLICATION, and if it exists,
executes it. If the procedure named APPLICATION does not exist, you see a
diagnostic and control goes to DCL.
The APPLICATION procedure is used to accomplish
any initializations and/or setup and then transfers control to the
top-of-the-line Pull-down Menu from which the rest of the application springs.
So the user's experience is that he or she selects the database from the list
and the next point of control is the application's Menu.
(You can make your application such that it is launched directly from the
desktop, bypassing this File Menu step altogether. For more information about
this, see "Procedures ." )
OPEN Options A, P and S
Cycle Errors: The four files that constitute the actual database are protected
with cycle numbers that must agree when a database is OPENed. The reason for
this is that if you ever restore a database from backup files you must restore
the four files that match, you cannot pick some of them from one backup and the
rest from another. Also, due to a power glitch or an OS glitch, the four files
can get out of synch (fortunately, this latter is very infrequent, but it has
happened to this author twice in the last 10 years).
If a cycle error happens, you are denied entry when you try to OPEN, and you
get appropriate diagnostics. Here are your possible recovery procedures:
If
it was caused by a mix-up during file restoration procedures, do it
again
and get it right.
You
can recompile the DBD with an S option (Recreate Option) which
saves
the data space but reinitializes structure space, so you must
rebuild
indexes with a STRUCTURE command after the recompile.
You
can open with the A option (e.g., OPEN/A). This lets you get into
the
database (you are in a read-only mode with the A option) so you
can
UNLOAD all the data. Then you can delete and rebuild the database from scratch.
The P option OPEN allows you to open the Procedure Catalog only, not the
database. You can then execute a procedure as long as that procedure only
contains commands that do not require an open database (commands such as
PROMPT, IF, CALC, SET, USERS, UNLOG, GOTO, etc.). This is ideal for an
automated un-log procedure to use when you can not open a database because of
max users. Also see MODE CHECKUNLOG .
The S option on OPEN says to open the database for exclusive use. You can't get
in until there are no other users, but once you are in, no one else can open
until you are through.
OPENing a Different Database from a Procedure
It is legitimate to execute a Procedure that contains an OPEN command. It could
either be opening a different database altogether, or a different Interface
(and therefore a different Catalog) to the current database.
When you do something like this, the next line (the first line after the OPEN
command) must be a procedure call referring to a Procedure in the new Catalog,
and that procedure call must have a Z option on it. The Z option tells us to
clean up, accomplish the transition, and start at the top of the stack in the
new catalog. For example, suppose this is a procedure in AAA:
:
:
OPEN
BBB
APPLICATION/Z
Control transfers to the new Catalog (BBB) and the APPLICATION procedure in BBB
is invoked. The Z option makes it all work. Control then stays in BBB, it does
not come back to the next line of AAA. Of course, BBB could have been a
full-path name.
Although this no longer has anything to do with OPEN, this seems like a good
place to mention that there is also a way to execute a procedure in a foreign
Catalog and have control return to the next line of the current procedure when
it is done. "See Shared or Common
Procedures ."
Copyright © 2019 , WhamTech, Inc. All rights reserved. This
document is provided for information purposes only and the contents hereof are
subject to change without notice. Names may be
trademarks of their respective owners.